Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotics are rapidly advancing, moving beyond mere human enhancement to mimic human-like behaviors. Following breakthroughs where scientists and researchers enabled AI-powered robots to perceive emotions and perform hazardous tasks, this technology now aims to replace humans in certain roles. The innovative “RoboChef” stands as a prime example of this evolution.
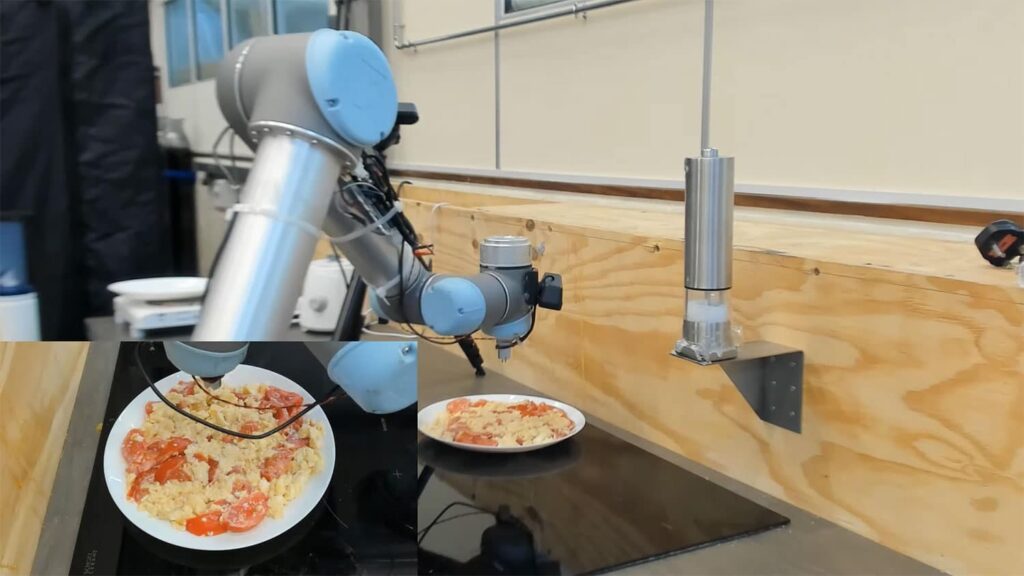
RoboChef, a pioneering robot developed by Cambridge University researchers, uniquely evaluates a food item’s saltiness across various stages of the chewing process. Unlike conventional electronic tasters, this advanced robot chef assesses salt content not just initially, but progressively as if chewing, providing a comprehensive understanding of the food’s flavor profile.
Introducing RoboChef: The Next Generation Culinary Robot
A collaboration between Cambridge University researchers and Beko, a leading domestic appliances manufacturer, has brought these advanced culinary robots to fruition. These robots are designed not only to distinguish between different food tastes but also to refine their cooking skills based on individual customer preferences. The ultimate vision is a future where RoboChef can prepare any requested dish, fulfilling a need often unmet in many existing culinary establishments.
The core innovation distinguishing this Robot Chef from existing electronic food-tasting machines lies in its “tasting as you go” methodology. While other devices offer only a static snapshot of a food’s salinity, RoboChef continually checks the balance of flavors throughout the simulated chewing process, precisely mirroring how humans perceive taste.
Expert Perspective: The Importance of ‘Tasting as You Go’ in Robotic Cooking
“Most home cooks will be familiar with the concept of tasting as you go – checking a dish throughout the cooking process to check whether the balance of flavours is right,” stated Grzegorz Sochacki from Cambridge’s Department of Engineering, the paper’s first author. “If robots are to be used for certain aspects of food preparation, it’s important that they are able to ‘taste’ what they’re cooking.”
Researchers suggest that replicating this intricate human process will ultimately lead to a more delicious final product. Just as human taste perception relies on saliva and digestive enzymes produced during chewing to determine food enjoyment, these robots have been meticulously trained to evaluate food taste at three distinct chewing stages.
Behind the Scenes: How the Robot Chef Learns to Taste
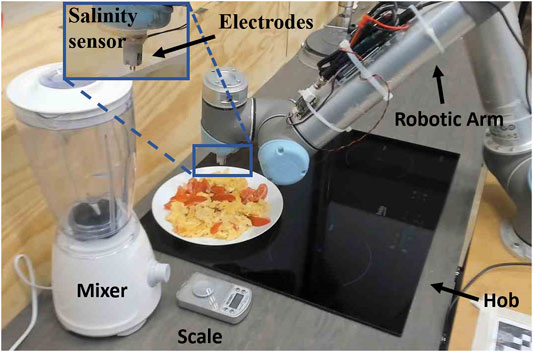
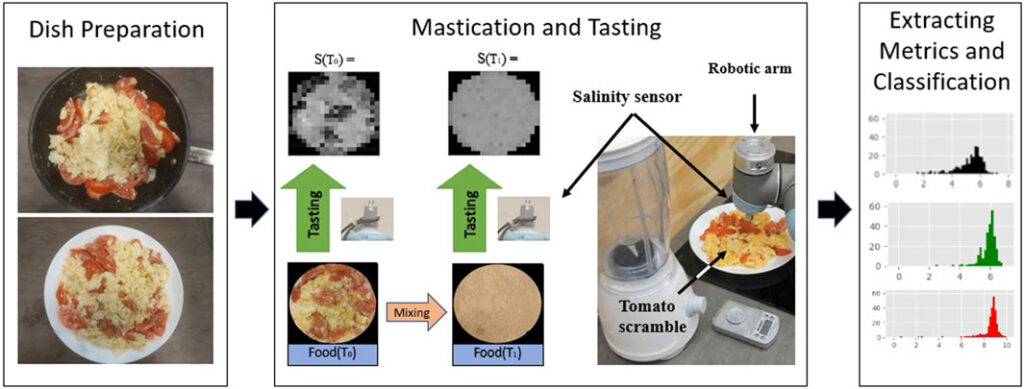
The initial challenge for the research team was training the robot to cook omelettes. Utilizing a salinity sensor attached to its arm, the robot was taught to taste nine different variations of scrambled egg and tomatoes at three simulated chewing stages. To accurately mimic the chewing progression, the egg mixture was blended, and the robot re-tested the dish.
Sochacki highlighted that the robot’s capabilities extend far beyond simply identifying if a dish is too salty or bland. It can, for instance, discern the need for more mixing or the addition of other ingredients to achieve optimal flavor.
Explore further: Scientists Create World’s First Self-Reproducing Robots
Ultimately, the robot successfully recorded distinct readings at various points of the chewing process, generating a comprehensive taste-map for each dish. This enabled it to develop a more nuanced understanding of flavors.
“In the end it’s just a single sensor which wouldn’t be able to do two different ingredients normally,” Sochacki explained to the BBC. “But thanks to chewing, we see all the different changes through mechanical processing.”
Engineer’s Perspective: The Science Behind RoboChef’s Taste
To enable the robot to accurately detect saltiness, researchers employed a conductance sensor, which effectively recreates the sensation of salinity. A conductance sensor measures the ease with which an electrical current flows through a sample. This is achieved by monitoring the current between two electrodes under a pre-determined voltage. The primary factor influencing conductivity is the movement of ions; thus, salinity increases with higher ion concentration, greater ion mobility, and stronger ionic charge. Given their affordability, robust design, and user-friendliness, salinity sensors are an excellent choice for robotic applications.
The research methodology was straightforward: food samples were placed on a non-conductive ceramic plate, allowing the salinity sensor to perform its analysis. The sensor efficiently executed its task, generating a detailed taste-map of the food.
However, it’s important to note the key distinctions between this robotic implementation and human taste perception of saltiness. The robot’s sensor lacks ion specificity, whereas human taste is selective for Na+ and K+ ions. Furthermore, the robot possesses the ability to pierce the sample, a capability that the human tongue, limited to tasting the surface, does not have.
The Future of Cooking: Robotic Innovations in the Kitchen
Addressing the question of whether robot chefs will become a reliable fixture in homes, Sochacki responded, “It’s definitely possible, but that’s probably a few years away.”
Explore More: Related Articles on AI and Robotics
Looking ahead, researchers aim to further develop the robot’s capabilities, teaching it to adapt to individual taste preferences, such as a fondness for sweet or oily foods. The ultimate goal is for these advanced culinary robots to become an indispensable part of modern households.
Dr. Muhammad Chughtai, a senior scientist at Beko, the domestic appliances manufacturer, who collaborated with the Cambridge University team, firmly believes this technology will play a pivotal role in homes in the foreseeable future.
He stated, “This result is a leap forward in robotic cooking, and by using machine- and deep-learning algorithms, mastication will help robot chefs adjust taste for different dishes and users.”
Indeed, as we look to the future, robot chefs are poised to become a central and transformative element in the kitchens of luxurious hotels and beyond.
Would you welcome robots into your kitchen to cook and assist you? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Join our community by subscribing to our Weekly Newsletter to stay updated on the latest AI updates and technologies, including the tips and how-to guides. (Also, follow us on Instagram (@inner_detail) for more updates in your feed).
(For more such interesting informational, technology and innovation stuffs, keep reading The Inner Detail).