Cloud computing represents the on-demand availability of various computing resources, primarily delivered via the internet. These essential resources typically include data storage (often referred to as cloud storage), robust computing power, databases, advanced networking capabilities, servers, and specialized software applications.
The fundamental concept behind cloud computing is simple: instead of relying on proprietary hard drives, databases and other resources are accessed through centralized servers over the internet. This approach allows authorized devices to connect and utilize these resources, fostering greater coherence and enabling significant economies of scale for both organizations and businesses. Cloud computing has become a top choice for many IT infrastructures due to its remarkable cost savings, enhanced manageability, reduced maintenance requirements, and the ability to rapidly adapt with high computing power. Notable examples of widely used cloud computing services include Microsoft OneDrive and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Understanding Cloud Computing Fundamentals
As previously mentioned, cloud computing empowers users to access crucial data and significant computing power remotely through various devices. This capability enables companies and businesses to securely store vast amounts of data in a remote cloud environment, which can then be accessed by multiple authorized users within the organization via the internet. Essentially, this data resides on a central server, which is meticulously installed and managed to provide seamless access to the cloud infrastructure.
Understanding remote cloud access involves two core concepts: virtualization and utilization. Virtualization refers to the creation of virtual versions of resources that are not physically present, such as virtual servers or devices. These virtual entities are configured and connected to physical servers, allowing them to be provisioned with computing services and resources as needed for efficient task execution. Virtualization significantly enhances the agility of IT operations and contributes to cost reduction by maximizing infrastructure utilization.

Consider a large company with extensive resources and services. It would be impractical to ensure every employee has direct access to thousands of gigabytes of resources from any location. However, by connecting to a cloud environment that centralizes all these facilities, the company can provide seamless access, making workflows simpler and more viable. This transformative technology is now also readily available to individual users.
Exploring Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud computing services are primarily offered through three distinct deployment models: private clouds, designed for a single organization; public clouds, accessible to multiple organizations or users; and hybrid clouds, which combine elements of both public and private environments.
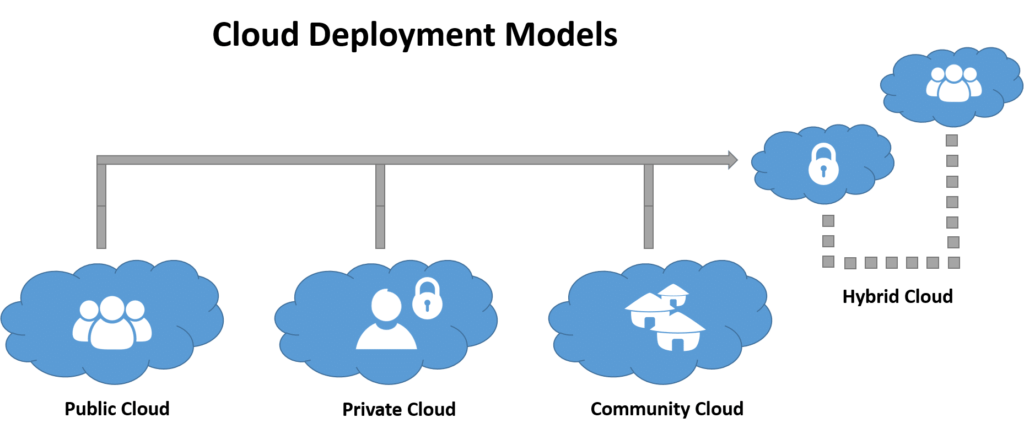
Private clouds are dedicated cloud infrastructures designed exclusively for a single business or organization. These environments can be managed internally by the organization’s IT team or by a third-party provider, and they can be hosted either on-premises or externally. Private clouds can significantly benefit businesses, though organizations must consider the substantial investment in data centers. Private cloud deployments often require dedicated physical space, specialized hardware, and human resources for ongoing management and maintenance, all of which contribute to the overall cost.
Public clouds are cloud environments that are openly available to the general public over the internet. These services are typically open access, with some even offering free tiers. Leading public cloud providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud (Aliyun) operate massive, centralized data centers that users can access remotely via the internet.
Hybrid clouds represent a strategic combination of a public cloud and a private environment, leveraging both private and public resources. This integrated model offers enhanced feasibility and flexibility, particularly concerning accessibility, data security, and compliance needs. A common example of a hybrid cloud involves interconnecting a private cloud with a public cloud service. This approach allows organizations to extend their cloud capabilities through seamless integration and customization across different cloud platforms.
Cloud bursting is a specific type of hybrid cloud strategy where an application running in a private cloud environment “bursts” or expands its capacity into a public cloud during periods of peak demand. This allows organizations to handle sudden increases in workload without over-provisioning their private infrastructure.
Community clouds involve shared infrastructure among several organizations that belong to a specific community and have common concerns, such as security protocols, compliance requirements, or jurisdictional mandates. These clouds can be managed either internally by the participating organizations or by a third-party provider, and they can be hosted internally or externally. While community clouds offer some cost savings compared to private clouds, the expenses are distributed among fewer users than in a public cloud, meaning the full economic benefits of cloud computing are not entirely realized.
Primary Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud computing services are delivered primarily through three fundamental service models: Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS).
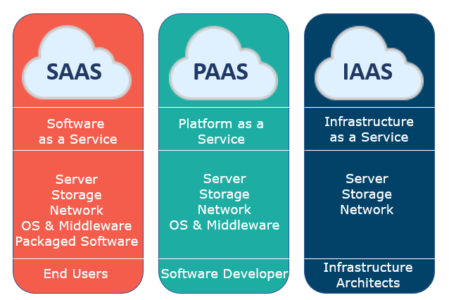
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): SaaS allows users to access software applications and databases over the internet, typically on a licensed, “on-demand” basis. Often referred to as “on-demand software,” these services can be acquired through a pay-as-you-go model or even be subscription-free. Popular examples utilizing this model include Microsoft Office 365 and Adobe Creative Cloud.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): IaaS providers, like Amazon Web Services (AWS), deliver foundational computing resources over the internet. This includes virtual server instances, scalable storage, and APIs that enable users to effortlessly migrate and manage their workloads on a virtual machine (VM). Users are provisioned with a specific storage capacity and maintain full control to start, stop, access, and configure their virtual servers and storage as needed. IaaS platforms typically offer a wide range of instance types, including small, medium, large, and extra-large options, as well as memory- or compute-optimized instances and customized configurations to meet diverse workload requirements.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): PaaS vendors provide a complete cloud environment that facilitates the development, running, and management of applications. This includes essential tools and channels such as programming languages, operating systems, databases, and web servers. With PaaS, consumers are relieved from managing or controlling the underlying cloud infrastructure, including the network, servers, operating systems, or storage. Instead, they retain control solely over their deployed applications and any specific configuration settings for the application-hosting environment.
Further Reading: Discover How Amazon Web Services Generates Billions from Cloud Computing
Key Features and Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Enhanced Agility: Cloud computing significantly boosts agility by allowing rapid provisioning and scaling of resources as needed, adapting quickly to evolving business demands.
- Performance Monitoring: Organizations can effectively monitor employee performance and system interactions through web services acting as the primary system interface.
- Increased Productivity: Cloud solutions enhance productivity by providing seamless remote access to virtual devices. Services like Google Drive and Microsoft OneDrive enable easy file access via the internet, eliminating concerns about inadequate device storage and facilitating essential data backups.
- Significant Cost Savings: Cloud computing offers substantial cost-saving potential for businesses of all sizes. Historically, companies had to invest heavily in purchasing, building, and maintaining expensive information management technology and infrastructure. With the cloud, these costly server centers and large IT departments can be replaced with efficient internet connections, allowing employees to access and complete tasks online.
- Improved Security (with caveats): Security can be bolstered through data centralization and dedicated security resources provided by cloud providers. However, organizations must remain vigilant regarding potential concerns, such as the loss of direct control over highly sensitive data and specific security considerations for operating system kernels.
Potential Limitations of Cloud Computing
- Limited Customization: Cloud services may sometimes offer limited customization options, potentially preventing them from perfectly aligning with a consumer’s specific operational or legal requirements.
- Privacy and Confidentiality Concerns: Privacy and confidentiality remain significant limitations within cloud computing. Users may feel a degree of insecurity when storing highly sensitive data, especially if it is not adequately encrypted or if concerns exist about data handling by the cloud provider.
- Security Risks: Since cloud computing relies on centralized servers, any unauthorized access or successful hacking attempt could lead to a catastrophic breach for the entire organization. Furthermore, physical disasters affecting the server infrastructure could also result in significant service disruptions and data loss.
Conclusion: The Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing continues to evolve as a transformative technology with immense scope and a market valuation reaching into billions. Global technology giants such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Alibaba extensively leverage cloud services for their business operations, optimizing efficiency and driving innovation.
References:
Join our community by subscribing to our Weekly Newsletter to stay updated on the latest AI updates and technologies, including the tips and how-to guides. (Also, follow us on Instagram (@inner_detail) for more updates in your feed).
(For more such interesting informational, technology and innovation stuffs, keep reading The Inner Detail).







Pingback: Future Technology Trends & Opportunities – The Inner Detail