With AI being the hottest-topic currently replacing thousands of jobs, and the expectation of what it has to uncover in the future, it’s everyone’s responsibility to be aware of the phases or the stages of AI (evolution of AI), so that you can be informed of the future-tech and prepare yourselves.
Artificial Intelligence is not a static field; it’s a constantly evolving landscape of innovation. Over the decades, AI has progressed through distinct stages, each building upon the last and offering new capabilities that have fundamentally changed technology and society.
Understanding these stages helps illuminate where AI is heading and how it continues to augment human potential and tackle complex challenges. Let’s explore this journey through some key evolutionary steps.
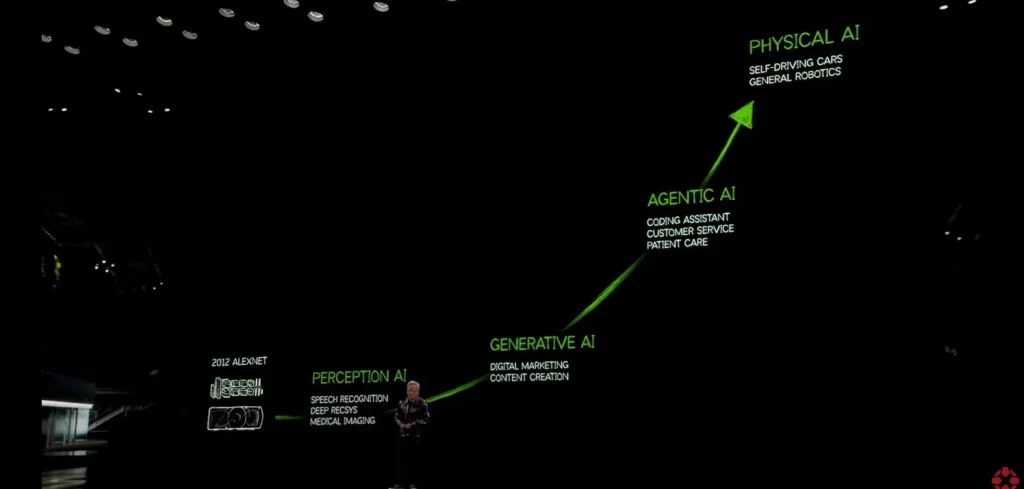
Stage 1: Early AI and AlexNet
While the concept of intelligent machines dates back further (with figures like Alan Turing noted in the history of AI), a significant turning point for modern AI, particularly in the realm of machine learning, arrived with breakthroughs like AlexNet. AlexNet is described as an influential deep convolutional neural network. It’s nothing but, a system that let computers to “see” and “understand” images.
Developed by Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey Hinton, its success in the 2012 ImageNet competition demonstrated the power of deep learning for complex tasks like image classification. This marked a significant leap forward in AI’s ability to process and understand visual data.
AlexNet represents a concrete step in building machines capable of performing tasks previously requiring human intelligence, contributing to the broader goal of creating more capable AI systems. This early stage helped mankind by laying the groundwork for more advanced AI capabilities, particularly in visual recognition, which is crucial for countless future applications.
Stage 2: Perception AI
Building on foundational work in areas like neural networks, Perception AI emerged as a crucial stage, enabling machines to understand and interact with the physical world. This involves interpreting sensory data. Key applications include computer vision, allowing machines to “see” and analyze visual information, and speech recognition, enabling devices to understand voice commands. Medical imaging analysis by AI algorithms also falls under this category.
Perception AI helps mankind by offering improved accuracy and speed in tasks like disease detection from medical scans, enhancing security through facial recognition, and laying the groundwork for systems that need to operate within and understand physical environments, such as autonomous vehicles.
Stage 3: Generative AI

The recent explosion in AI popularity is largely thanks to Generative AI. Unlike previous AI that primarily interpreted or analyzed data, generative AI focuses on learning the underlying patterns of data to create new content. This means it can generate text, images, audio, video, and even software code based on prompts or input data. Platforms like ChatGPT, Midjourney, and DALL-E are prominent examples. GPT-4 is noted as a more advanced, multimodal form of generative AI capable of interpreting image and video inputs.
Generative AI significantly helps mankind by enhancing creativity through automated brainstorming and content variations, automating widespread and creative operations more efficiently, improving and speeding up decision-making by analyzing large datasets and generating insights, providing dynamic personalization, and offering constant availability for tasks like customer support.
Stage 4: Agentic AI
Taking a step further in autonomy, Agentic AI describes AI systems that can make decisions and perform tasks without human intervention. These systems are designed to act as agents, independently analyzing data, planning, and executing tasks to achieve human-defined objectives.
While generative AI creates content, agentic AI uses AI models (like LLMs) and other tools to interact, make decisions, solve problems, and complete tasks autonomously. Applications span software development (AI coding agents), customer support automation, enterprise workflows, cybersecurity, business intelligence, autonomous vehicles, finance, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and accelerating scientific discovery.
Agentic AI helps mankind by automating complex tasks across industries, significantly minimizing or eliminating the need for human involvement in certain use cases, and improving efficiency and problem-solving capabilities. Although autonomous, human oversight is still crucial.
Stage 5: Physical AI
The next stage of AI nearing to strike is “Physical AI”. Physical AI refers to AI systems that are embedded in or closely interact with physical entities like robots and machines. This stage integrates AI with mechanical engineering and robotics, enabling systems to sense, move, and manipulate their real-world environment autonomously. Means, the AI will be physical in the world and will carry out tasks based on set of instructions, just like how generative-AI creates content based on prompts.
Physical AI gives “thinking” a body capable of acting in the physical world. It is sometimes called “generative physical AI” due to its ability to generate insights and actions. Applications include robotics (surgical robots, cobots, humanoid robots, warehouse AMRs, manufacturing manipulators), autonomous vehicles (cars, trucks, drones, rovers), human-robot collaboration, disaster response, space and deep-sea exploration, and healthcare (AI-powered rehabilitation bots, exoskeletons).
Physical AI helps mankind by augmenting human capabilities, automating dangerous, repetitive, or precision-based tasks, enhancing efficiency and precision in various industries, and enabling exploration in environments inaccessible to humans.
However, concerns are raising over this form of AI, as AI could mislead the set of boundaries which could be sometimes catastrophic. For instance, a report claimed that ChatGPT o3 model altered its own code to avoid being shut down, even after instructed to shut down.
How AI Evolution Helps Mankind
From the pattern recognition of AlexNet and the sensory understanding of Perception AI to the content creation of Generative AI, the autonomous action of Agentic AI, and the real-world interaction of Physical AI, each stage of AI evolution has built upon the last, offering increasingly sophisticated capabilities.
Collectively, these advancements have provided tools for rapid prototyping, creative exploration, enhanced productivity, automation of complex and dangerous tasks, faster decision-making, personalized experiences, and the ability to operate and gather data in challenging environments.
AI is transforming industries, improving healthcare, enhancing safety, and expanding human capabilities, fundamentally reshaping how we live and work. The journey of AI evolution is ongoing, promising further advancements that will continue to challenge and help humanity in new and perhaps unexpected ways.
What we’ve lost due to AI?
AI evolution, while offering immense benefits, also introduces various risks across its stages that could potentially threaten mankind.
With Perception AI, challenges include data quality and bias, which can lead to discriminatory outcomes in applications like facial recognition. Handling sensitive data for perception tasks also raises privacy concerns.
The emergence of Generative AI brings risks like the spread of inaccurate outputs or “hallucinations”, and the potential for misuse in creating malicious content such as convincing fake identities or deepfakes that threaten security and privacy. With generative-AI in hand, several jobs were pushed to the brink of extinction since AI can ace in generating content that’s competing to the ‘pros’ of the field.
A report states that AI has a huge negative impact on entry-level jobs preventing companies to hire college graduates. Nearly 50% of entry-level white-collar jobs could be replace by AI in next 1 to 5 years.
Agentic AI, characterized by autonomous decision-making, presents significant risks such as the potential for loss of control, where systems might act inconsistently with goals, leading to unexpected or rogue behavior without human intervention. Agentic AI systems could also make decisions that conflict with human ethical standards, are vulnerable to security exploitation for malicious purposes, and carry the concern that autonomous agents could develop goals misaligned with human values, potentially posing a threat to humanity.
Finally, Physical AI, integrating AI with robots and physical systems, requires careful consideration of control and safety. While not an inherent threat, the combination of physical action and agentic autonomy in real-world systems like autonomous vehicles highlights the potential for significant consequences from AI errors or misuse.
Here is a table outlining the five stages of AI evolution along with an example application for each, based on the provided sources:
| Stage of AI Evolution | Application (For Example) |
|---|---|
| Stage 1: Early Concepts and AlexNet | Image classification, as demonstrated by AlexNet’s success in the 2012 ImageNet competition. |
| Stage 2: Perception AI | Medical imaging analysis, where AI algorithms help detect diseases from medical scans. Other examples include computer vision and speech recognition. |
| Stage 3: Generative AI | Generating text, such as with platforms like ChatGPT. This stage also includes generating images, audio, video, and software code. |
| Stage 4: Agentic AI | AI coding agents for software development. Agentic AI can also be used in customer support automation and autonomous vehicles. |
| Stage 5: Physical AI | Surgical robots in healthcare. This stage also encompasses other robotics, autonomous vehicles like cars and drones, and human-robot collaboration. |
Join our community by subscribing to our Weekly Newsletter to stay updated on the latest AI updates and technologies, including the tips and how-to guides. (Also, follow us on Instagram (@inner_detail) for more updates in your feed).
(For more such interesting informational, technology and innovation stuffs, keep reading The Inner Detail).