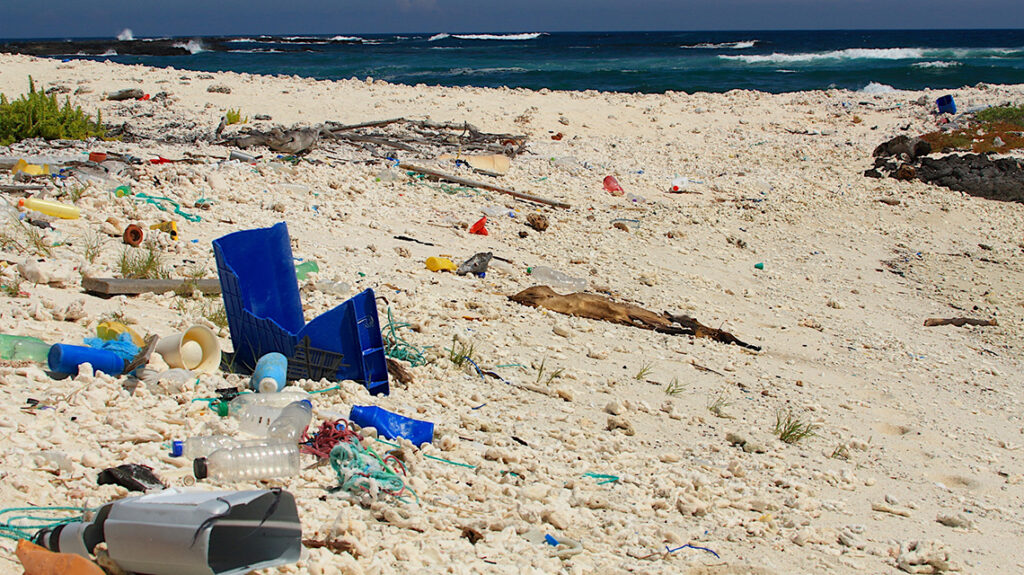
Our planet is drowning in plastics, the commodious hazard to the land and oceans, in about 300 million tons every year, the peak number ever since the origin of earth.
As world is now aware of, plastics creating substantial threat to mother earth, consuming centenary years to degrade, researches gone onset to exclude the use of it, or to make it viable and eco-friendly. And the outcome been creation of plastic, that completely breaks down in sunlight, in just a week.
The novel plastic material, developed by researchers from China’s Hauzhong University of Science and Technology, got decomposed rapidly in sunlight from a petroleum-based polymer into succinic acid, a naturally occurring nontoxic small molecule that has no microplastics left behind in the environment.
Degradable Plastic was an accident
The researchers discovered that the polymer (named poly deca-4,6-diynedioic acid) or PDDA, being capable of degrading with help of sunlight and oxygen, remains stable in the dark without oxygen.
The degradable plastic had been accidentally emerged into this earth, is what staggering element here. When Liang Luo, co-author of the research, first developed the plastic in 2020, he intended it to change color with pH, for use as a chemical sensor. However, he noticed that the plastic’s natural deep red color faded quickly and the plastic film broke apart over several days in sunlight.
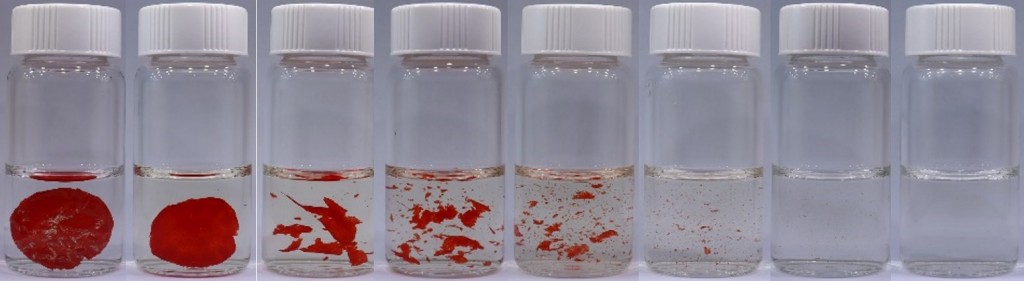
In cases of polymers as this, which is a long-chained compound (made of many monomers) with alternating double & single bonds, the color appears from its molecular structure – long chains of monomers – rather than a dye. Breaking down into monomers when exposed to sunlight, as indicated by loss of that color, proves the degrading ability of this plastic polymer – could be the future plastics, researchers hope.
In aim of understanding the chemistry of the plastic’s break-down, they used NMR to characterize the polymer’s structure based on its magnetic field. The characterization also conforms the same.
Sunlight irradiation breaks the polymer’s double and triple-bonded carbon backbone.
Application
This unique molecular structural plastic, thought won’t be really perfect for single-use plastics or plastic bottles, owing to its degradability in sunlight, it could only be potential in places where it’s dark without oxygen. Flexible electronics or smartphones where they would often be isolated from air and light when sealed inside it, could be the application for this polymer.
Instances of throwing it away as e-waste, makes it less harmful as the plastic components would fade away in sunlight.
“We will continue to explore the degradation of plastics,” Luo says, looking ahead.
Though he doesn’t have a timeline for commercialization, he says the ballpark “could be 5 or 10 years.”
The rapid digital development with advances of artificial intelligence and machine learning, demands has been triggered exponentially to combat the climate change, for making the world, a better place in future. And biodegradable plastic is such a demanded contrivance today, combating climate-change.






